In the rapidly evolving tech landscape, the role of a product manager has become increasingly vital. A product manager is responsible for guiding a product from conception through its lifecycle to its launch and beyond. This role requires a blend of strategic vision, user-centric design, and business acumen. An online course that covers the entire spectrum of product management—from design to launch—can equip aspiring product managers with the necessary skills and knowledge. Here’s a comprehensive guide to what such a course should include and why it’s beneficial.
1. Understanding Product Management

Overview: The foundation of any product management course is an in-depth understanding of what product management entails. This includes the responsibilities of a product manager, the skills required, and the typical challenges faced in this role.
Key Topics:
- Role and Responsibilities: Understanding the day-to-day tasks and strategic responsibilities of a product manager.
- Skills and Competencies: Key skills such as leadership, communication, analytical thinking, and market knowledge.
- Product Lifecycle: An overview of the stages in a product’s lifecycle—from ideation to end-of-life.
Why It’s Important: A solid grounding in these basics provides context for more advanced topics and helps students understand the broad scope of the product management role.
2. Market Research and Analysis

Overview: Effective product management starts with understanding the market. This includes identifying customer needs, analyzing competitors, and recognizing market trends.
Key Topics:
- Customer Research: Techniques for understanding customer needs and pain points, such as surveys, interviews, and focus groups.
- Competitive Analysis: Identifying and analyzing competitors’ strengths and weaknesses.
- Market Trends: Keeping abreast of industry trends and technological advancements.
Why It’s Important: Market research informs product strategy and helps ensure that the product meets customer needs and stands out in the market.
3. Product Ideation and Conceptualization
Overview: Once market opportunities are identified, the next step is to generate and refine product ideas.
Key Topics:
- Brainstorming Techniques: Methods for generating creative product ideas.
- Idea Validation: Testing and validating ideas through prototypes and minimum viable products (MVPs).
- User Personas: Creating detailed profiles of target users to guide product development.
Why It’s Important: Effective ideation and conceptualization ensure that the product ideas are viable and aligned with market needs.
4. Product Design and Development

Overview: This stage involves translating ideas into tangible products through design and development.
Key Topics:
- User Experience (UX) Design: Principles of designing intuitive and user-friendly interfaces.
- Product Specifications: Defining the technical and functional requirements of the product.
- Agile Development: An overview of agile methodologies, including Scrum and Kanban, for iterative development.
Why It’s Important: A well-designed product is critical for user satisfaction and market success. Agile development ensures flexibility and responsiveness to changes.
5. Product Strategy and Roadmap
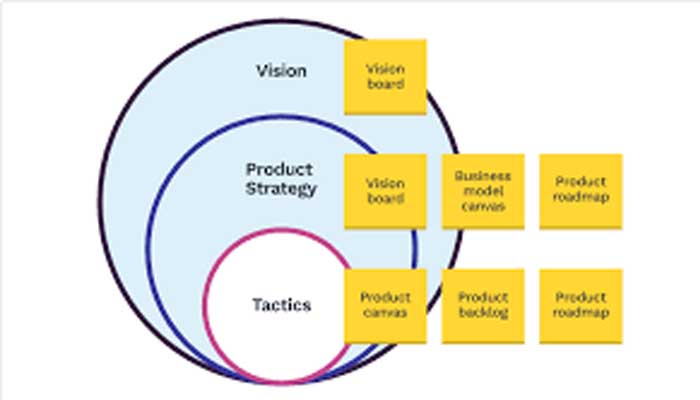
Overview: Developing a strategic plan and roadmap is essential for guiding the product through its lifecycle.
Key Topics:
- Vision and Goals: Defining the long-term vision and specific goals for the product.
- Roadmap Development: Creating a detailed plan outlining the stages of product development and key milestones.
- Prioritization Techniques: Methods for prioritizing features and tasks based on impact and feasibility.
Why It’s Important: A clear strategy and roadmap ensure that the product development stays on track and aligned with business objectives.
6. Project Management and Execution

Overview: Managing the execution of the product development plan involves coordinating teams, resources, and timelines.
Key Topics:
- Project Planning: Creating detailed project plans with timelines, tasks, and resources.
- Team Management: Techniques for leading and managing cross-functional teams.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating potential risks that could impact the project.
Why It’s Important: Effective project management ensures that the product is developed on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards.
7. Product Launch and Go-to-Market Strategy
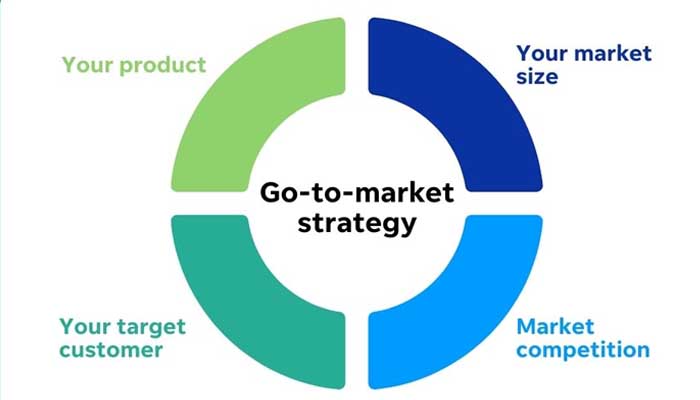
Overview: Launching the product involves preparing the market, sales teams, and customers for the new product.
Key Topics:
- Launch Planning: Developing a comprehensive plan for launching the product.
- Marketing and Promotion: Strategies for marketing the product and generating buzz.
- Sales Enablement: Equipping sales teams with the tools and knowledge to sell the product effectively.
Why It’s Important: A successful product launch maximizes market impact and sets the stage for the product’s success.
8. Post-Launch Management

Overview: Managing a product post-launch involves monitoring performance, gathering feedback, and making necessary improvements.
Key Topics:
- Performance Metrics: Identifying and tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure success.
- Customer Feedback: Collecting and analyzing feedback from customers to identify areas for improvement.
- Product Iteration: Continuously improving the product based on feedback and performance data.
Why It’s Important: Post-launch management ensures that the product remains competitive and continues to meet customer needs.
9. Case Studies and Real-World Applications

Overview: Applying theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios through case studies and practical exercises.
Key Topics:
- Successful Product Launches: Analysis of successful product launches and the strategies behind them.
- Product Failures: Learning from product failures to understand common pitfalls and how to avoid them.
- Hands-On Projects: Practical exercises and projects to apply learned concepts.
Why It’s Important: Case studies and hands-on projects provide practical insights and reinforce learning by applying concepts to real-world situations.
Conclusion
A comprehensive product management course that covers the journey from design to launch equips aspiring product managers with the skills and knowledge needed to succeed in this dynamic field. Such a course should include a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application, covering everything from market research and ideation to product launch and post-launch management.
Investing in an online course with a well-rounded curriculum can open doors to numerous career opportunities in product management. Whether you are new to the field or looking to enhance your existing skills, mastering these key areas will prepare you to lead products to success in the competitive tech landscape of 2024 and beyond.
